ABSTRACTS
Faster to the Resuscitation: Air vs Ground TransportationAuthor: Elizabeth Lacy | | Associate Authors: John T. Simpson | Juan Duchesne | Tom Dransfield | Emily Nichols | Danielle Tatum | Jacob Broome | David Rayburn
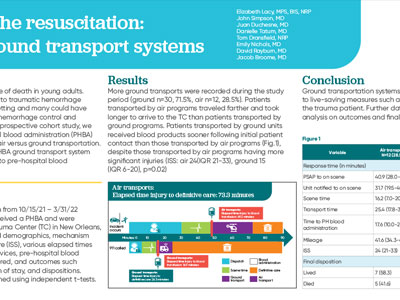
Introduction Trauma is the leading cause of death in young adults. At least 50% of deaths due to traumatic hemorrhage occur in the prehospital setting and many could have been prevented with early hemorrhage control and resuscitation. In this limited prospective cohort study, we are comparing prehospital blood administration (PHBA) systems of transportation: air vs ground transportation. We hypothesize that the PHBA ground transport system will provide quicker access to prehospital blood administration. Methods Prospective data collection from 10/15/21 to 3/31/22 of trauma patients who received a PHBA and were transported to a Level I Trauma Center (TC) in New Orleans, LA. Data elements included demographics, mechanism of injury, Injury Severity Score (ISS), various elapsed times relevant to prehospital services, prehospital blood volume and units administered, and outcomes such as mortality, hospital length of stay, and dispositions. Univariate analyses performed using independent t-tests. Results More ground transports were recorded during the study period (ground N = 30, 71.5%, air N = 12, 28.5%). Patients Transported by air programs traveled farther and took longer to arrive to the TC than patients transported by ground programs. Patients transported by ground units received blood products sooner following initial patient contact than those transported by air programs, despite those transported by air programs having more significant injuries (ISS: air 24 (IQR 21-33), ground 15 (IQR 6-20), P = 0.02).
Conclusion
|